India’s Union Budget and its investment implications on India equities

The Event: India’s Union Budget
This Union Budget marks the first budget of the current government after securing a third consecutive term in office, indicating stability and continuity in the policy framework.
India’s finance ministry expects a healthy real GDP growth of 6.5-7% in FY2025.1
We believe that economic growth will remain robust in India, driven by both domestic and manufacturing activities. Exports of goods will be supported by improving global demand while services exports will continue to grow with cost efficiency.
Key policy focus
1. Employment is the key
Job creation is the focus in the budget the government proposed 2 trillion Rupees allocation for job creation over 5 years, addressing unemployment, education and skilling.2
The budget outlined 3 employment-linked fiscal incentives to both employees and employers, aimed at boosting job creation in both demand and supply side. This includes first time employees subsidy, reimburse to employer contribution and substantial job hiring in manufacturing sector.
The employment incentives also target labor-intensive manufacturing sectors and provides credit support for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), which should help stimulate hiring in the private sector.
The government will also introduce a comprehensive scheme to offer internship opportunities in the top 500 companies to ten million young people over the next five years.3
2. Capital Expenditure continues
The government continue to show commitment on capital expenditure, capex outlay for infrastructure retained at the interim budget target of 3.4% of GDP.4
The policy framework for long-term economic development aims to pave the way for the next generation of factor market (land, labor, capital, and technology) reforms. This will be implemented in collaboration with state governments.
Reforms in sectors like power, manufacturing and electronics will continue. Custom tax on some minerals and gold/silver will be reduced to boost domestic manufacturing and promote exports.
To drive land reforms, the government will digitize land records and maps to assist urban local bodies, while providing appropriate fiscal support for these land reform initiatives.
These reforms are expected to boost employment levels and subsequently promote domestic consumption through higher income
3. Further fiscal consolidation
The government continue to lower the fiscal deficit target to 4.9% of GDP for FY25, and below 4.5% of GDP by FY26 which underscores the government’s commitment to economic stability and growth.5
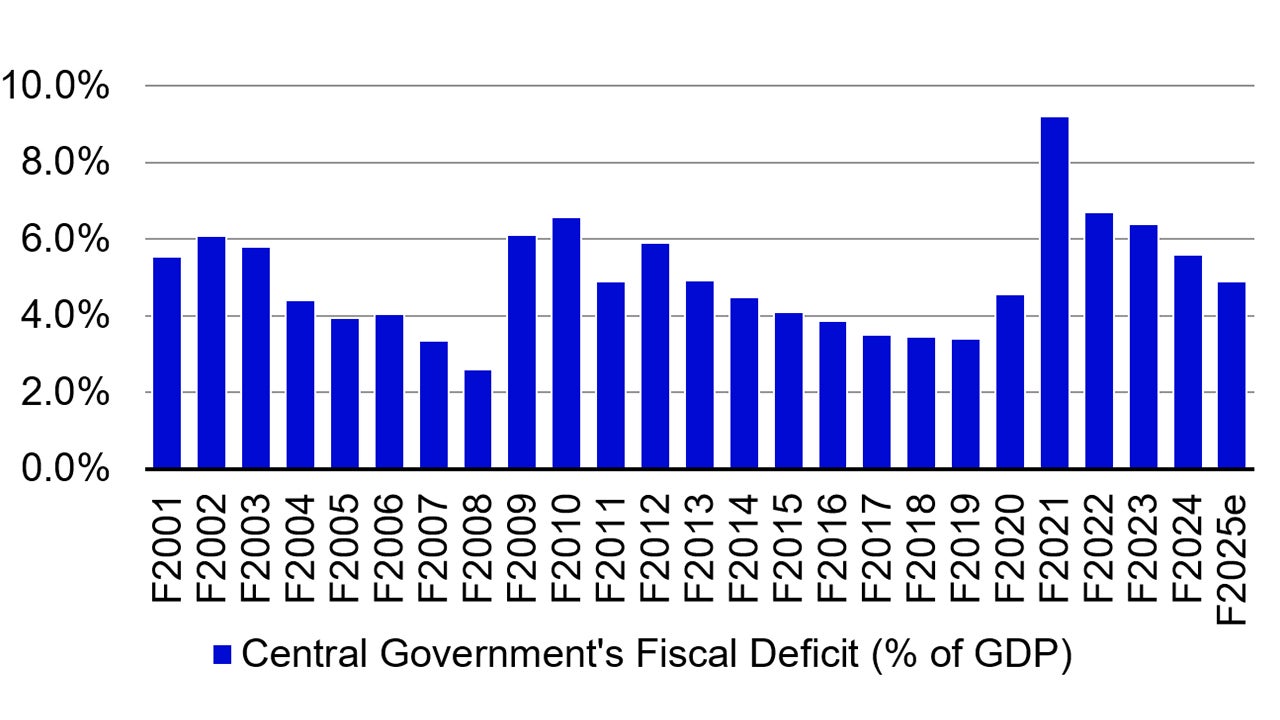
Source: Goldman Sachs, 23 July 2024
This gradual deficit reduction strategy embodies a prudent fiscal approach, balancing the demand for economic stimulus with the imperative of long-term financial stability.
A lower fiscal deficit reduces the government’s debt and potentially leading to lower interest rates and creating more room for private sector investment.
Moreover, this fiscal discipline bolsters India's credibility in global financial markets, possibly resulting in upgraded sovereign credit ratings by rating agencies and attract more foreign investment.
The budget’s focus areas align well with the positive outlook of the Indian market, its emphasis on welfare, job creation, and economic stability are expected to fuel growth in the manufacturing sector and boost domestic demand.
Investment implications
The policy direction announced by the government aligns well with the anticipated trajectory for India's future economic development.
We continue to be positive on 3 major trends in India with strong growth potential: Manufacturing renaissance, Consumer explosion and Financial transformation.
1. Manufacturing Renaissance
As supported by the continuation of reforms and upskilling of labour, manufacturing sector in India is expected to increase efficiency and boost production. India has the capacity to boost its trade. India is forecasted to export goods worth US$ 1 trillion by 2030 and is on the road to becoming a major global manufacturing hub. 6
The manufacturing sector could potentially create 85 million more jobs, providing a big boost for income and a multiplier for economic growth.
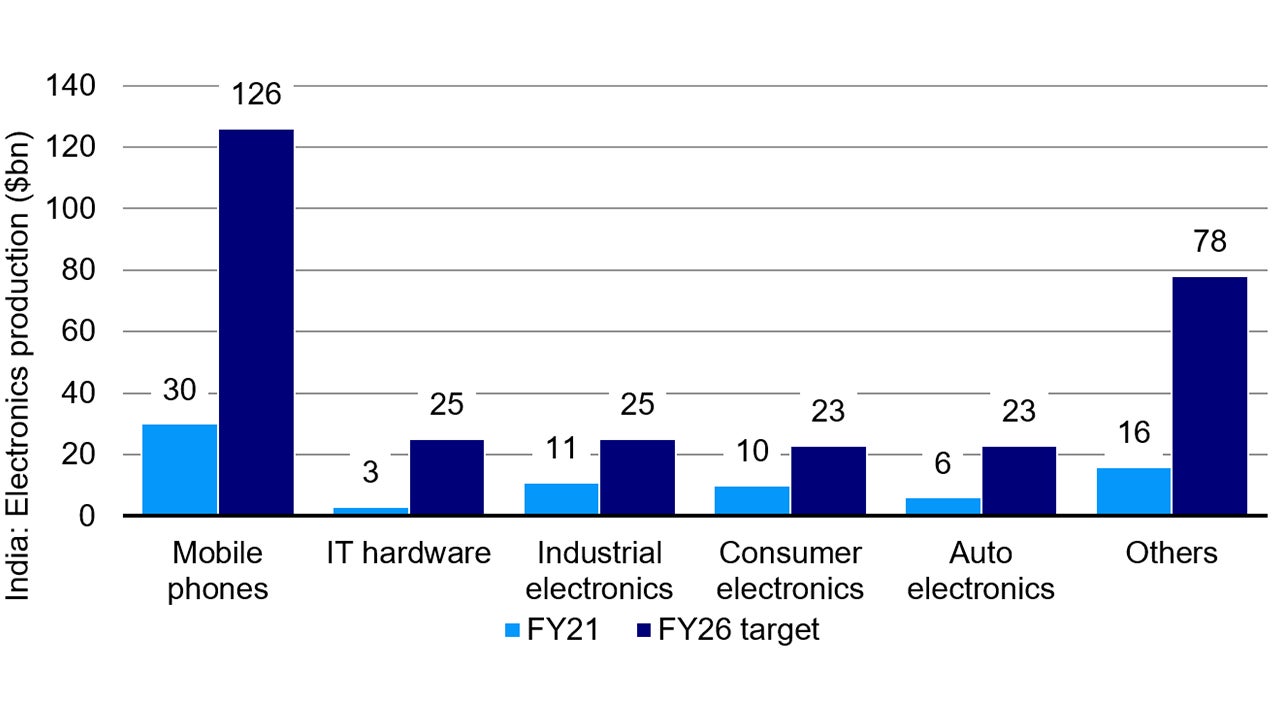
Source: Government of India, Jefferies, as of June 2024
2. Consumption Explosion
Domestic demand will continue to benefit with more employment and incentives schemes. An increasing number of middle to high-income households and stable job market are driving overall private consumer expenditure growth. We believe a shift in consumption patterns in India will increase demand for discretionary goods and services.
3. Financial transformation
Financial transformation, with improving digital infrastructure will continue to gain from urbanization of India. Greater demand for digital banking, mobile payments, investments towards digital finance, coupled with the growth of fintech innovations, are all expected to drive financial inclusion across India.
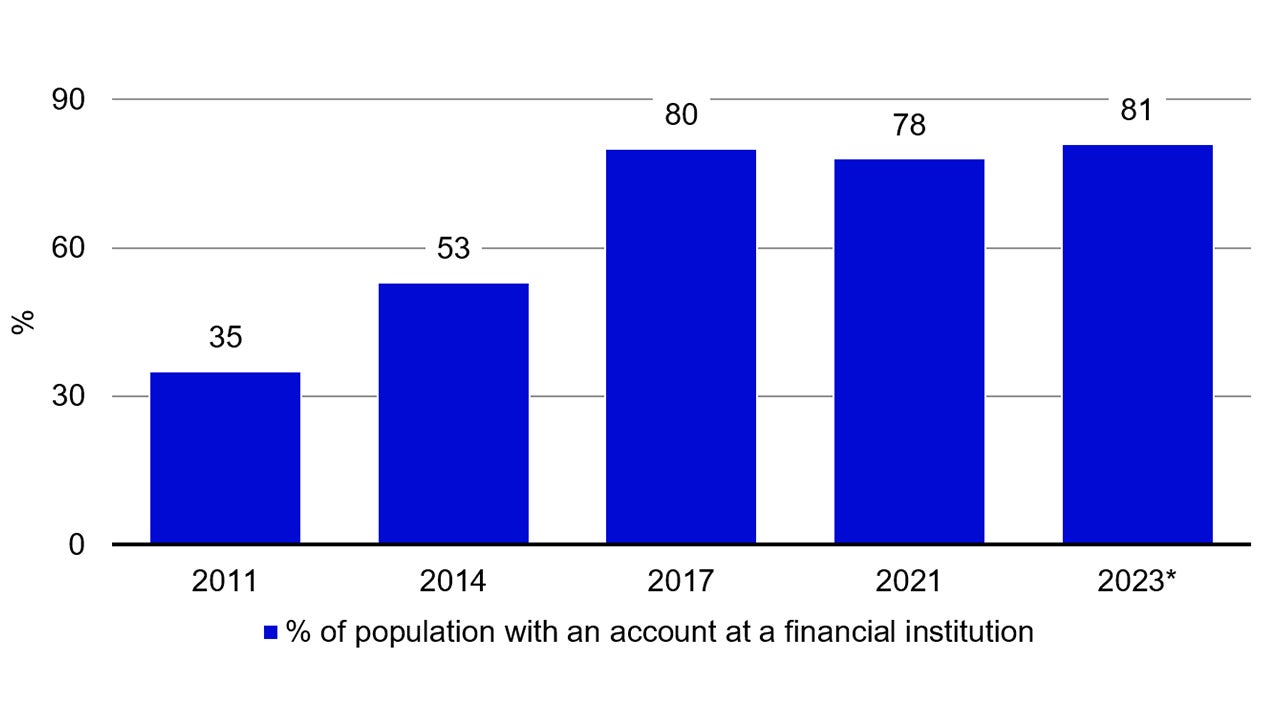
Source: World bank, Global Findex database, Dec 2023. *2023 data is based on UBS estimates
Investment risks
The value of investments and any income will fluctuate (this may partly be the result of exchange rate fluctuations) and investors may not get back the full amount invested.





