
Markets and Economy Higher earnings visibility and growth offered by domestic sectors
In China, we expect the domestic economy to fully recover and, at the same time, US-China tensions to continue for the foreseeable future.

Digital trend is supported by improving infrastructure spend and innovative corporate strategies.
Compared to five years ago, the average download speed of mobile broadband in China has increased by about six times while the fee for mobile internet (mobile phone users accounted for 99% of the internet users) has dropped by over 90 percent. A faster internet service at lower cost has greatly boosted usage growth. China is now a digital society with more than 900 million internet users (figure 1). It has pledged to invest more than US$3.78 trillion in new digital infrastructure over the next 5 years1. In 2020 alone, as much as US$423 billion has already been allocated to projects including 5G base stations, data centres and artificial intelligence.

The digital trend is very evident. A Chinese consumer’s daily life involves frequent engagements with different types of online platforms offering both products and services. This has encouraged many internet companies to use innovative strategies to engage consumers. The importance of the digital trend can be seen in the MSCI China index composition where the communication services and consumer discretionary sectors constitute more than 20% of the index. The large companies in these sectors are mainly in the internet space.
A good example is our holding in an online platform which is capitalising on the growing digitalisation of consumer markets. Despite being a late comer to the food delivery market, the company gained market share from its competitors to become the number one platform for food delivery. Using this position, it has been successful in cross-selling higher-margin lifestyle services in leisure and entertainment.
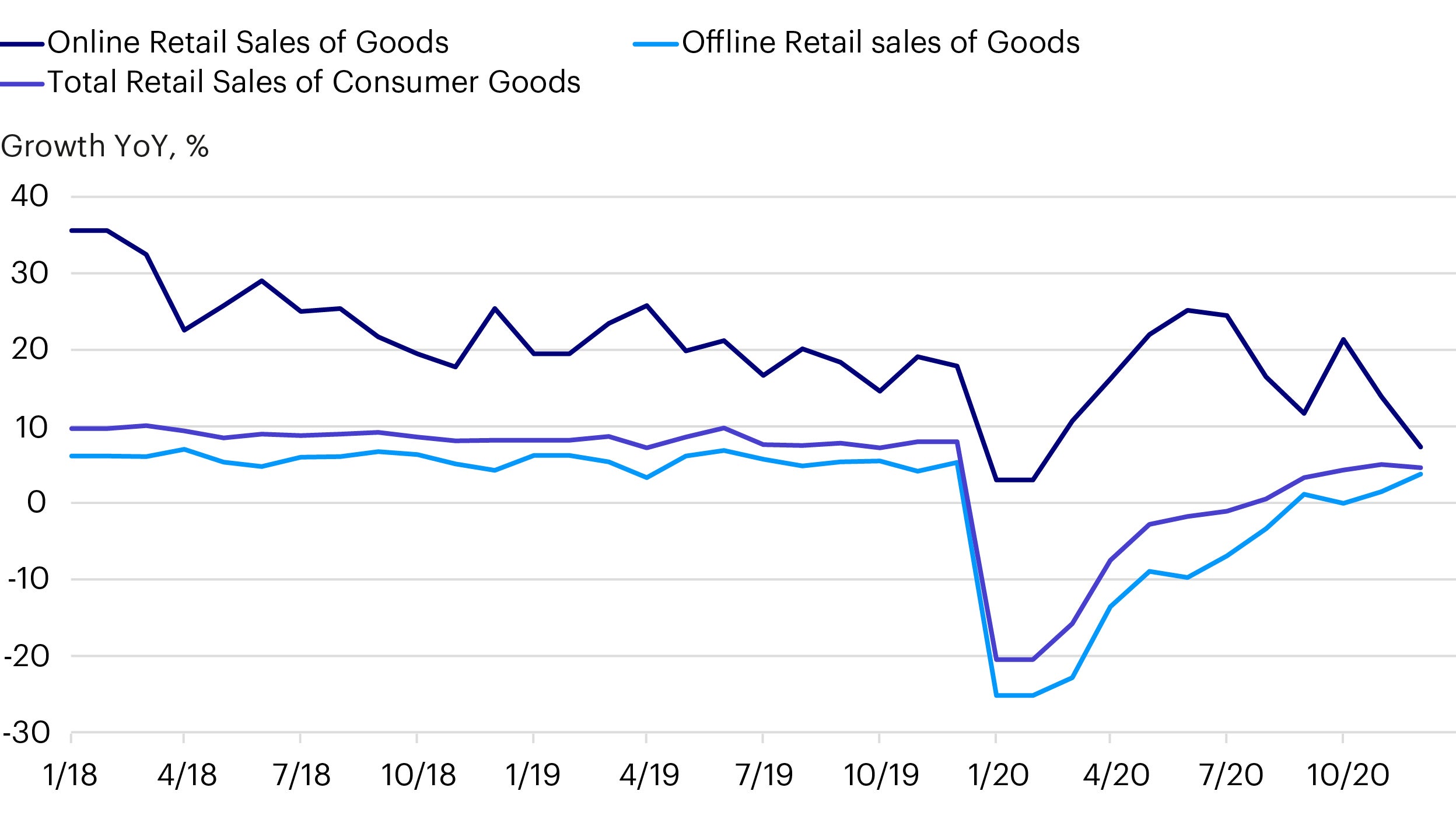
The Covid-19 outbreak is accelerating the digital trend by encouraging the purchasing of products and services on-line. E-commerce platforms acted fast to capitalise on this growth by launching a new shopping festival, Double Five, throughout which customers were provided with discounts and incentives to generate strong sales growth. The Covid-19 outbreak also encouraged other new strategies. For instance, a leading internet conglomerate (a holding) introduced an international version of its cloud-based video conferencing tool in more than 100 countries to capture market share. These strategies resulted in the e-commerce retail sales growth remaining resilient during Covid-19 (figure 2).
The Covid-19 backdrop also led to the emergence of new markets such as the telemedicine market. During the crisis, e-commerce platforms, which had previously just delivered drugs or booked appointments, began to provide treatment and advice. For example: a subsidiary of our holding in a large online platform claimed that monthly consultations had grown tenfold since the outbreak: an arm of another large platform (a holding) launched a free “online clinic”; and WeDoctor, an app backed by a leading internet conglomerate (a holding) mobilised 20,000 physicians to work online during the epidemic thereby encouraging the use of its platform going forward.

In China, we expect the domestic economy to fully recover and, at the same time, US-China tensions to continue for the foreseeable future.

Our investment strategy favours private enterprises. They are highly competitive and innovative, constantly utilising new technologies to deliver market leading products and services.