
Markets and Economy Markets take Supreme Court tariff ruling, US-Iran tensions in stride
Markets largely expected last week’s tariff decision and the flare-up in US-Iran tensions, while new US economic data was weaker than anticipated.
Global growth has been moving above trend with broad strength across most major regions, marking the first shift into an expansion regime since 2022. Equity markets began the year with strong momentum as cyclical companies and smaller stocks outpaced more defensive characteristics. This performance has been supported by steady global activity, contained inflation, and a policy environment that remains constructive. Steeper yield curves across developed markets suggest easier financial conditions ahead and raise the likelihood of a longer economic cycle.
Overall, the combination of rising growth and stable inflation creates a favorable backdrop for risk assets. A diversified approach across sectors and regions remains important to maintain an overweight to equities while avoiding expensive segments of the US market.
In response to the stronger environment, we favor increasing risk by further overweighting equities relative to fixed income. Within equities, we continue to favor cyclical sectors and mid‑sized companies. In fixed income, we maintain an overweight in credit, reduce duration, and prefer emerging markets debt. We also remain positioned for potential softness in the US dollar, with selective preferences across developed and emerging market currencies.
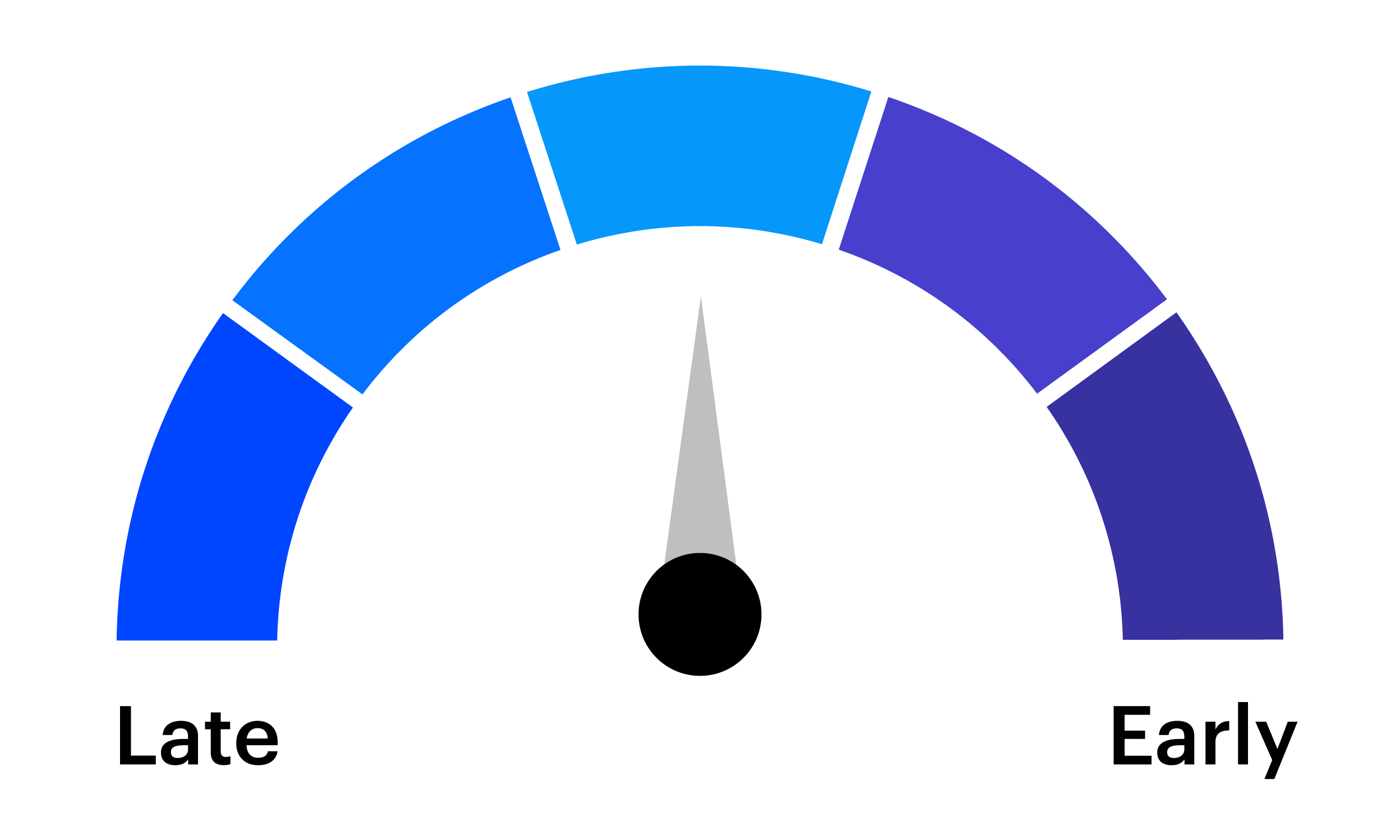
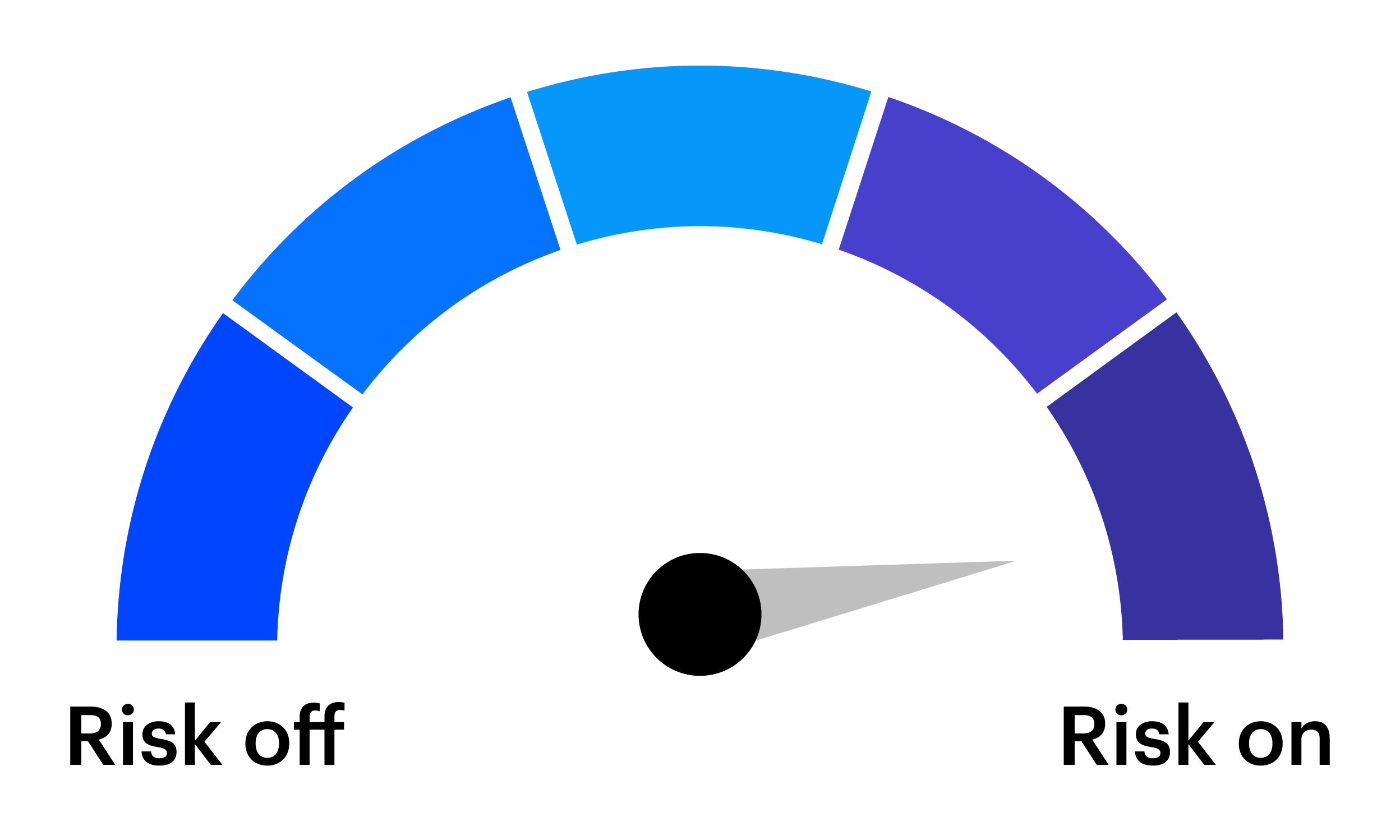
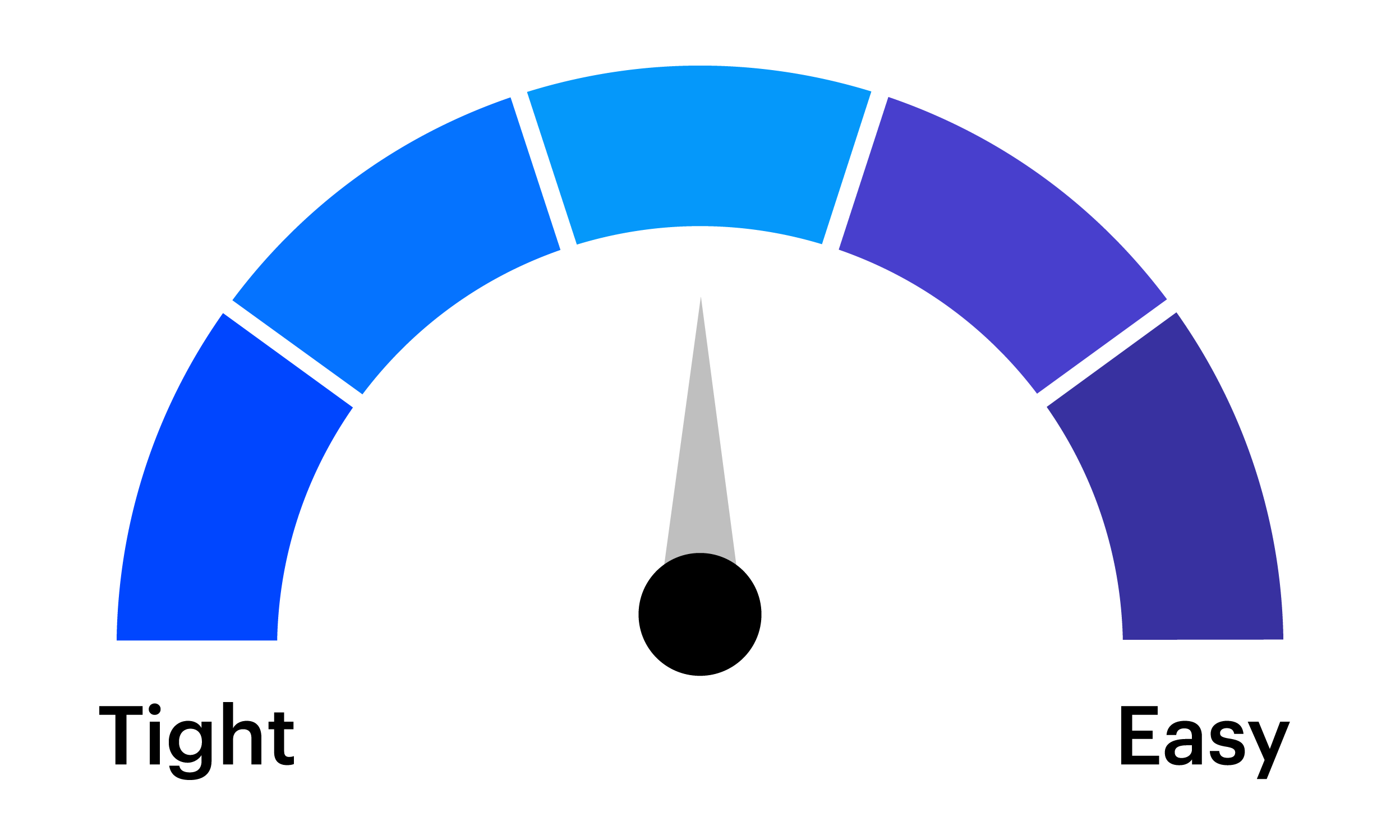


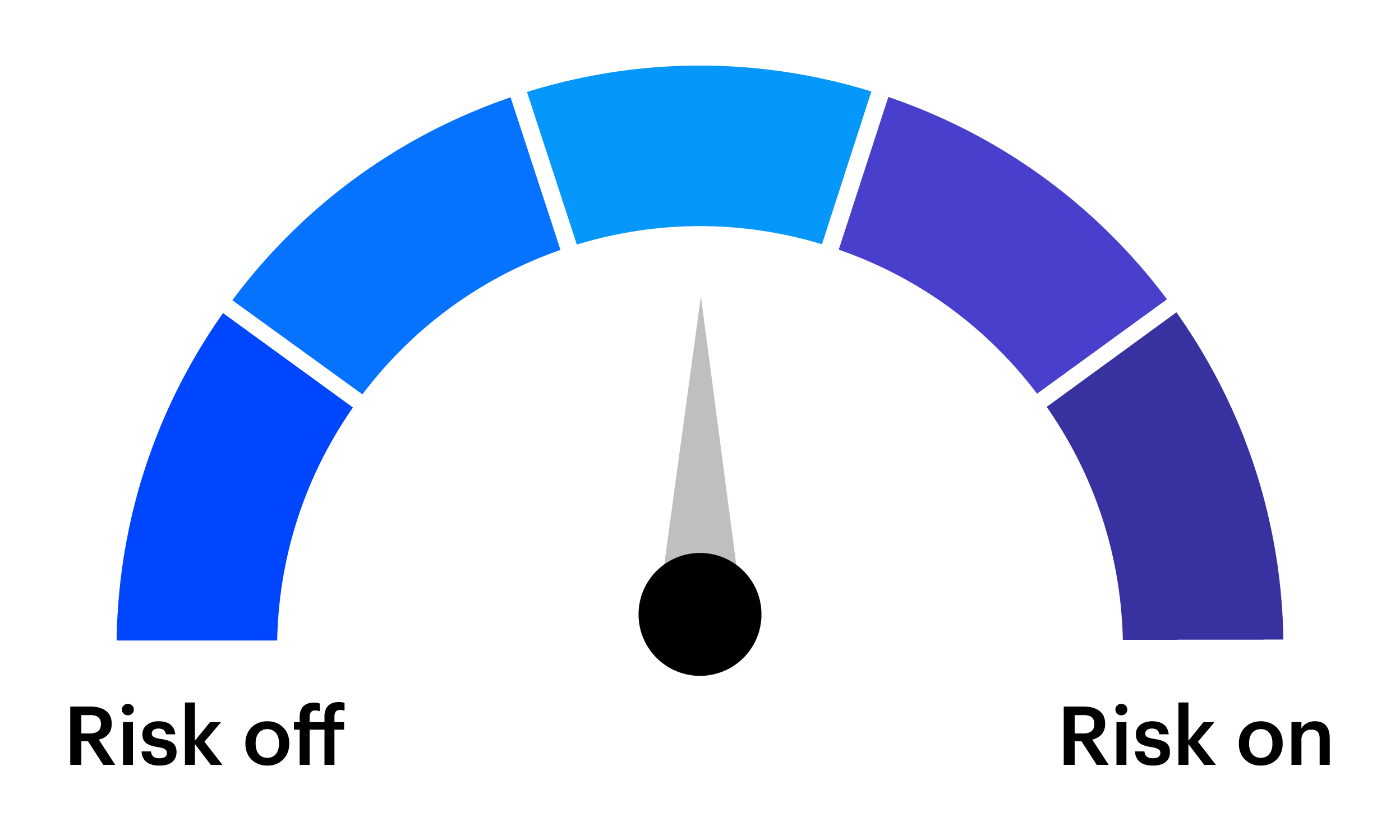
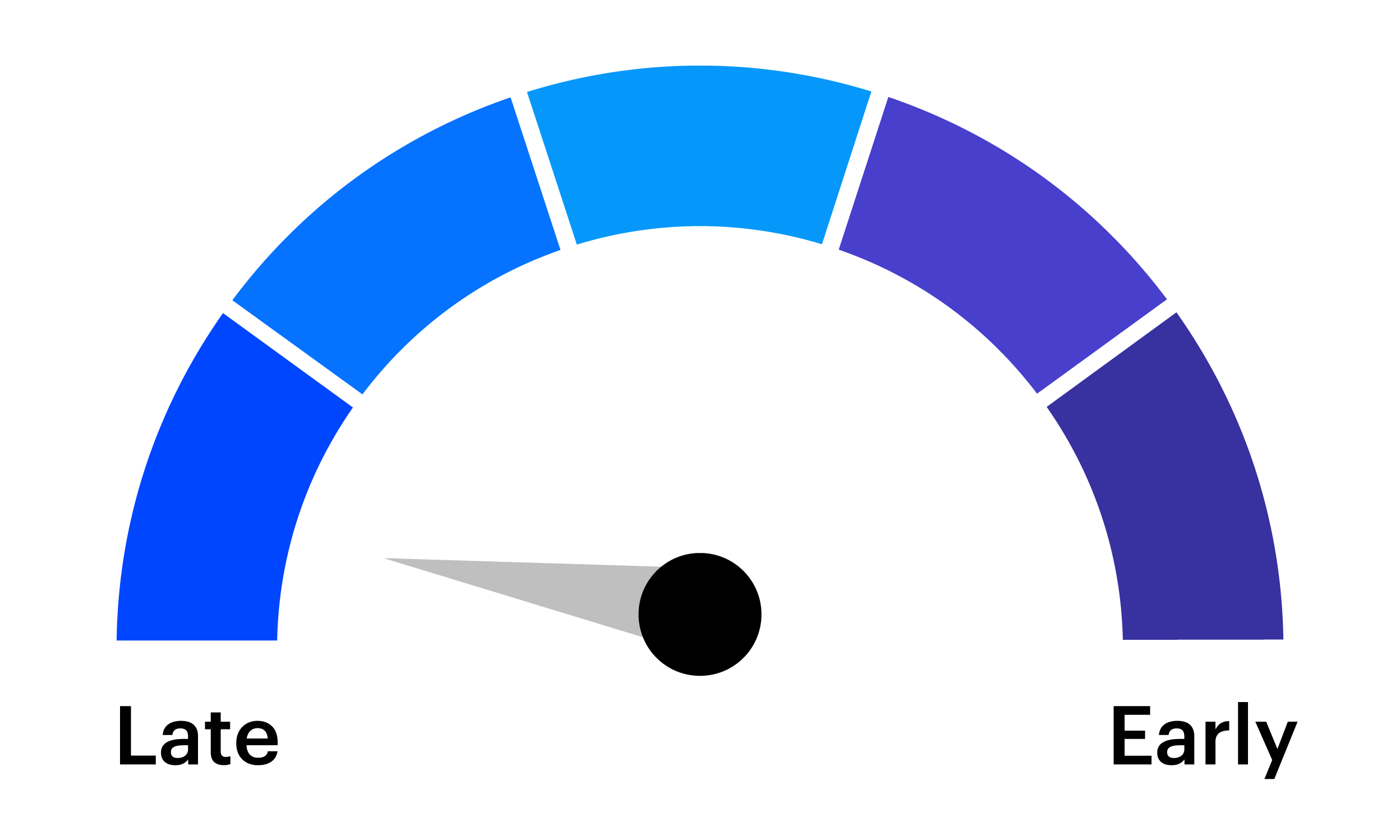
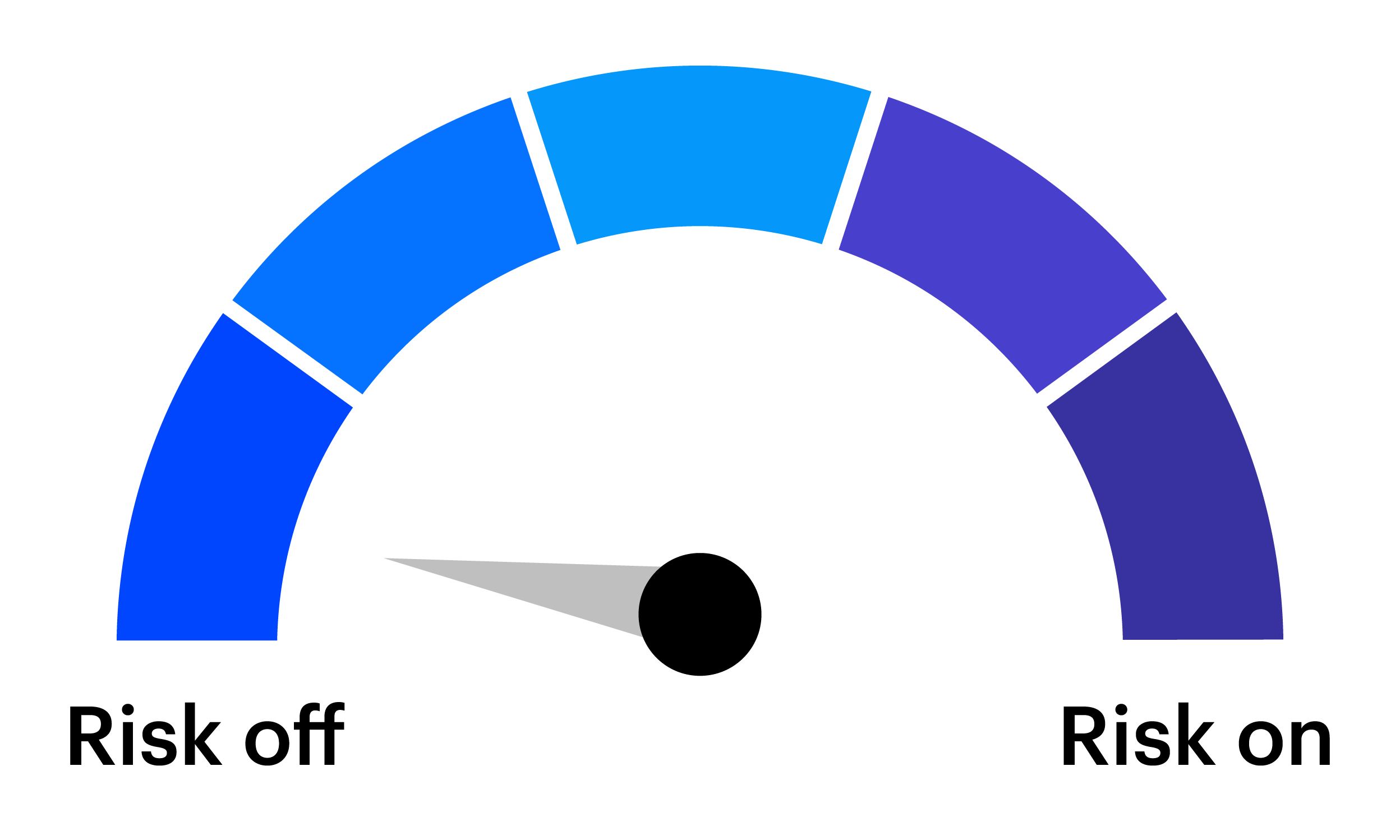
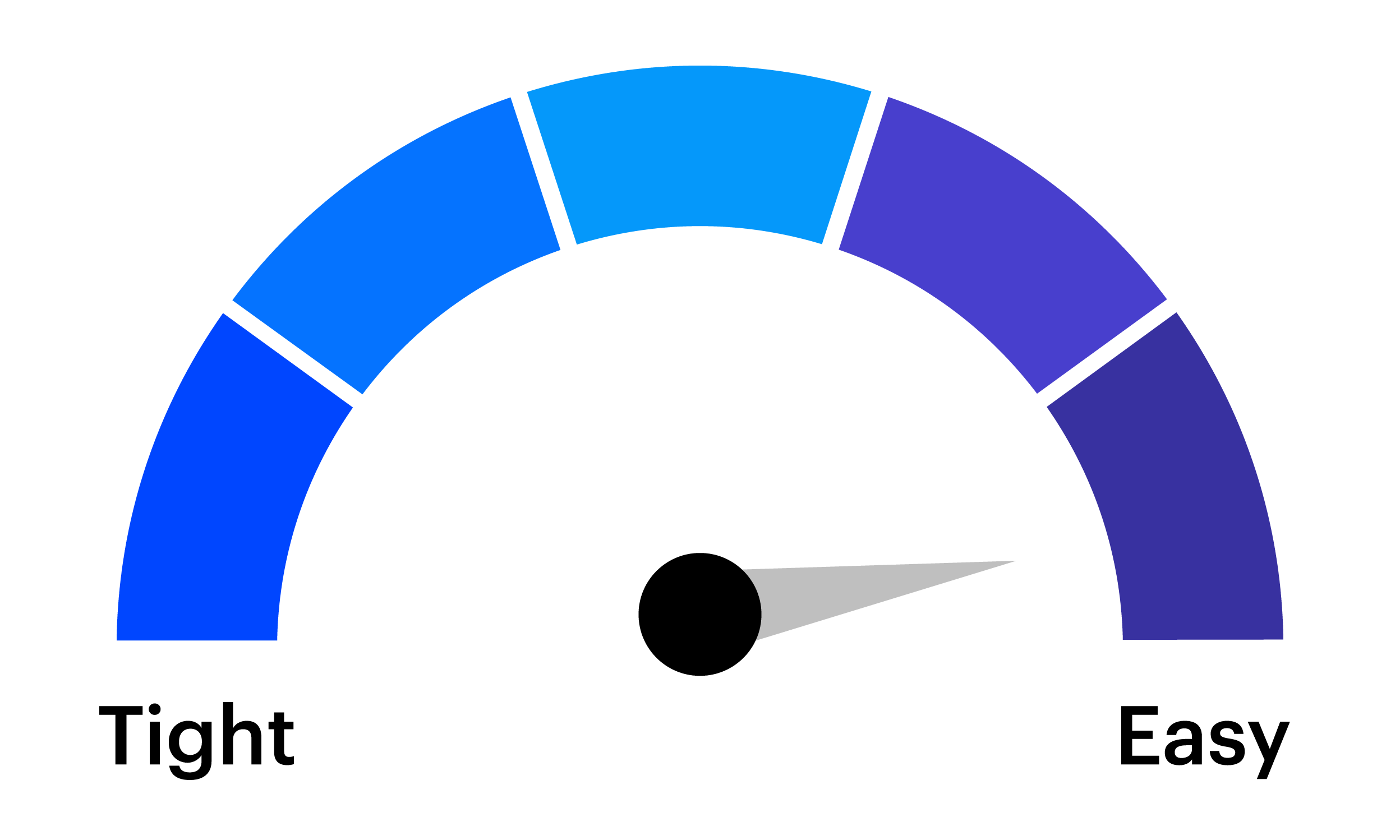
A challenge for tactical investors is preparing for the expected and anticipating the unexpected. The tactical asset allocation (TAA) framework from the Invesco Solutions team is designed to enhance a long-term strategic asset allocation (SAA) by making portfolio tilts based on near-term market views.
The tactical, dynamic factor rotation shown below is also utilized in the Invesco Russell 1000® Dynamic Multifactor ETF (OMFL).
Explore further research and analysis from our market and investment experts.

Markets largely expected last week’s tariff decision and the flare-up in US-Iran tensions, while new US economic data was weaker than anticipated.

The US Supreme Court struck down IEEPA tariffs, but alternative statutes may mean tariffs remain, although the market impact appears limited.

On one side, weaker growth makes Fed easing more likely. On the other side, stronger growth supports an intact business cycle. Either can be supportive of markets if inflation stays contained.
NA5191803
Diversification does not guarantee a profit or eliminate the risk of loss.
Many products and services offered in technology-related industries are subject to rapid obsolescence, which may lower the value of the issuers.
Larger, more established companies may be unable to respond quickly to new competitive challenges such as changes in consumer tastes or innovative smaller competitors. Returns on investments in large capitalization companies could trail the returns on investments in smaller companies.
An inflation-protected security is a type of fixed-income investment that guarantees a real rate of return. This means the annual percentage return realized is adjusted for changes in prices due to inflation or other external effects.
Class Y shares are closed to most investors. Please see the prospectus for more details.
Tightening is a monetary policy used by central banks to increase interest rates to slow economic growth and curb inflation.
Investments focused in a particular sector, such as technology, are subject to greater risk, and are more greatly impacted by market volatility, than more diversified investments.
This does not constitute a recommendation of any investment strategy or product for a particular investor. Investors should consult a financial professional before making any investment decisions.
Past performance does not guarantee future results. An investment cannot be made directly into an index.
All investing involves risk, including the risk of loss.
Some products are offered through affiliates of Invesco Distributors, Inc.
The opinions referenced above are those of the author as of February 2026. These comments should not be construed as recommendations, but as an illustration of broader themes. Forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future results. They involve risks, uncertainties, and assumptions; there can be no assurance that actual results will not differ materially from expectations.
Tightening is a monetary policy used by central banks to normalize balance sheets.
There are risks involved with investing in ETFs, including possible loss of money. Index-based ETFs are not actively managed. Actively managed ETFs do not necessarily seek to replicate the performance of a specified index. Both index-based and actively managed ETFs are subject to risks similar to stocks, including those related to short selling and margin maintenance. Ordinary brokerage commissions apply. The Fund's return may not match the return of the Index. The Fund is subject to certain other risks. Please see the current prospectus for more information regarding the risk associated with an investment in the Fund.
The S&P 500® Index is an unmanaged index considered representative of the US stock market.
The Russell 2000® Index measures the performance of small-capitalization stocks and is a trademark/service mark of the Frank Russell Co.®.
The S&P 500® Quality Index screens holdings based on three fundamental measures of quality: Profitability, earnings quality, and financial robustness — which helps to assess a company’s potential future profitability, as well as the financial risk each company faces.
The S&P 500® Value Index consists of stocks in the S&P 500® Index that exhibit strong value characteristics based on three measures: Book value-to-price, earnings-to-price, and sales-to-price.
The S&P 500 cyclical indexes focus on the cyclical sectors of the S&P 500, which include industries like consumer discretionary, financials, industrials, information technology, and materials, that are heavily influenced by economic cycles.
Growth stocks tend to be more sensitive to changes in their earnings and can be more volatile.
A value style of investing is subject to the risk that the valuations never improve or that the returns will trail other styles of investing or the overall stock markets.
Stocks of small- and mid-sized companies tend to be more vulnerable to adverse developments, may be more volatile, and may be illiquid or restricted as to resale.
Fixed income investments are subject to credit risk of the issuer and the effects of changing interest rates. Interest rate risk refers to the risk that bond prices generally fall as interest rates rise and vice versa. An issuer may be unable to meet interest and/or principal payments, thereby causing its instruments to decrease in value and lowering the issuer’s credit rating.
The yield curve plots interest rates, at a set point in time, of bonds having equal credit quality but differing maturity dates to project future interest rate changes and economic activity.
Credit spread is the difference between Treasury securities and non-Treasury securities that are identical in all respects except for quality rating.
Alternative products typically hold more non-traditional investments and employ more complex trading strategies, including hedging and leveraging through derivatives, short selling and opportunistic strategies that change with market conditions. Investors considering alternatives should be aware of their unique characteristics and additional risks from the strategies they use. Like all investments, performance will fluctuate. You can lose money.
The risks of investing in securities of foreign issuers, including emerging market issuers, can include fluctuations in foreign currencies, political and economic instability, and foreign taxation issues.
Junk bonds involve a greater risk of default or price changes due to changes in the issuer’s credit quality. The values of junk bonds fluctuate more than those of high quality bonds and can decline significantly over short time periods.
In general, stock values fluctuate, sometimes widely, in response to activities specific to the company as well as general market, economic, and political conditions.
Municipal securities are subject to the risk that legislative or economic conditions could affect an issuer’s ability to make payments of principal and/ or interest.
An investment in emerging market countries carries greater risks compared to more developed economies.